Collagen – for what and for whom?
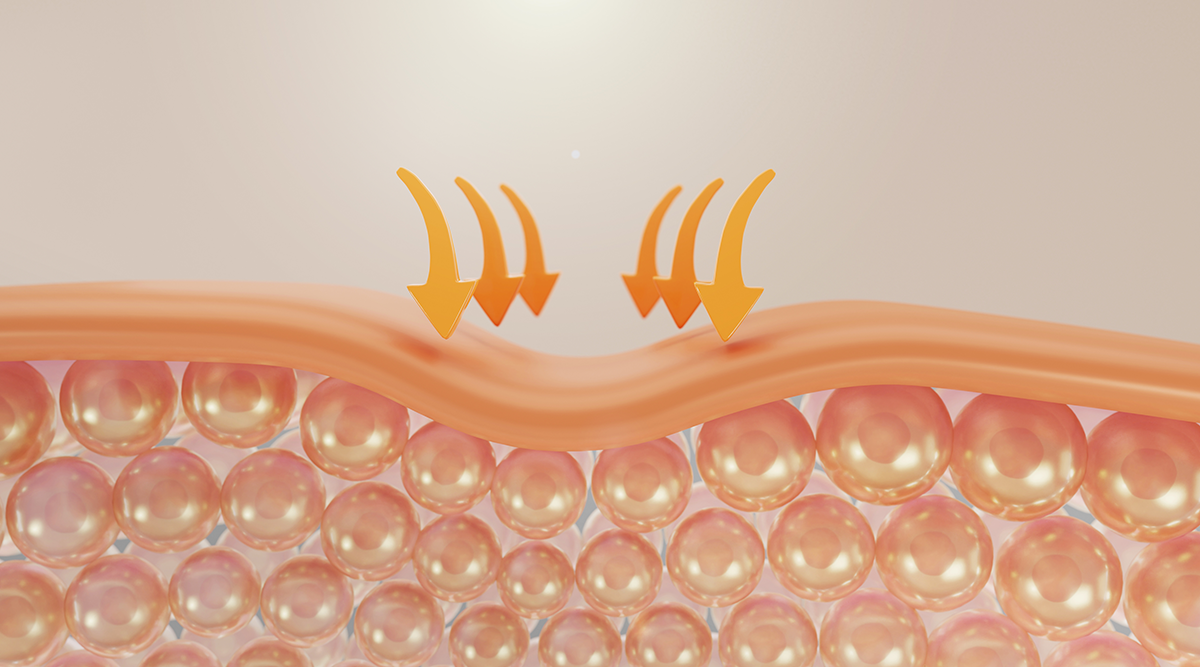
What is collagen?
Collagen is the most important protein, making up as much as a third of all the proteins in our bodies. That’s why it has many varied and important roles to play. On the one hand, collagen strengthens bones, and on the other, it is an important building block of connective tissue (the connective tissue that makes up our tendons, joints, skin and muscles).
In recent years, collagen-containing supplements have gained a firm place in many people’s menus, but is their popularity justified? It seems to be. Their benefits have been scientifically proven in a number of ways, for example, by improving skin condition and reducing joint pain. You can read more about the promising properties of collagen below.
Collagen as a skin regenerator
Collagen makes up the lion’s share of our skin. Its role is to strengthen the skin, and to some extent to keep it elastic and hydrated. Over the years, however, collagen in the body becomes less and less abundant, leading to dry skin and wrinkles.
Some studies have shown that collagen-containing supplements are highly effective in combating skin problems. In one trial, women took 2.5-5 grams of collagen per day in supplement form, for 8 consecutive weeks. During this time, they noticed that their skin was less dry and much more supple compared to women who had not taken collagen.
At the end of the second trial, which lasted 12 weeks, daily supplementation with a drink was found to have moisturised the skin of female subjects and visibly reduced their wrinkles. The latter is thought to be due to the fact that the collagen ingested stimulates the body to produce collagen itself. It is also possible that other proteins needed for skin building are involved in this process. Supplements containing collagen may therefore be a good anti-ageing tool, but should be limited to 10-15 grams of collagen per day.
Joint pain reliever
In addition to the skin, collagen is found in cartilage, the fibrous tissue that protects joints. Unfortunately, as collagen is less abundant in mature age, there is a greater risk of joint disease, such as osteoarthritis, creeping in. Here, too, collagen supplements can be a lifeline, as a number of trials have shown. In addition to osteoarthritis, general joint pain can also be relieved.
In one study, adults were given 2 grams of collagen a day for 70 days in a row. Compared with participants who had not taken collagen, the collagen users had improved health by the end of the trial, with significantly less joint pain and greater mobility. Apparently, the same thing happens in cartilage as in the skin: collagen accumulates there and stimulates the body to produce collagen itself. This reduces inflammation and pain and protects the joints better. In general, it has been found that a daily amount of 8 to 12 grams should be sufficient to initially reduce joint pain, and 10 to 15 grams thereafter.
Strong bones
Collagen is one of the main building blocks of our bones. It acts as a supporting framework to help keep them strong. As the amount of collagen in bone decreases over time, so does the bone mass. This can lead to the development of a bone disease, such as osteoporosis, which is characterised by lower bone density and a higher risk of fracture.
But science gives hope. Ingested collagen has the potential to prevent bone breakdown, increase bone mineral content and reduce the amount of protein in the blood (excess protein breaks down bones).
Increased muscle mass
Those with sarcopenia, or age-related loss of muscle mass, can also benefit from extra collagen. Collagen makes up 1-10% of our muscle tissue and this protein is needed to keep muscles strong and able to perform their tasks successfully.
Based on research, scientists have concluded that collagen is involved in the synthesis of proteins found in muscles, such as creatine, and helps muscles to get stronger and bigger after exercise, in short – to grow muscle mass.
Supporter of HeartWork
While collagen is already helpful enough on many fronts, it is also involved in the heart, and more specifically the arteries. Arteries carry blood from the heart to all parts of the body, and collagen’s role is to ensure that their walls are strong and tight.
When the collagen content in the artery wall decreases, it becomes fragile. This can lead to artery blockage, or arteriosclerosis. In more severe cases, this can lead to a heart attack or stroke. It is thought that collagen-containing supplements can prevent artery blockages and other cardiovascular diseases.
Marine collagen or bovine collagen?
Supplements on the market usually contain one of two collagens: either marine collagen or bovine collagen. However, the difference between the two is quite small. Namely, marine collagen contains more of the first and second types of collagen, while bovine collagen is composed of the first and third types. Another difference is the starting material. Marine collagen is mainly produced from fish skins, roes and skeletons, whereas bovine collagen is produced from cowhide and connective tissue.
The collagen in supplements is mostly hydrolysed, or broken down into its constituent parts, which makes it easier for our bodies to absorb. It has also been found to be safe for health and is convenient and easy to take as a food supplement. As a promising tool, collagen should be tried by anyone with the concerns mentioned above.