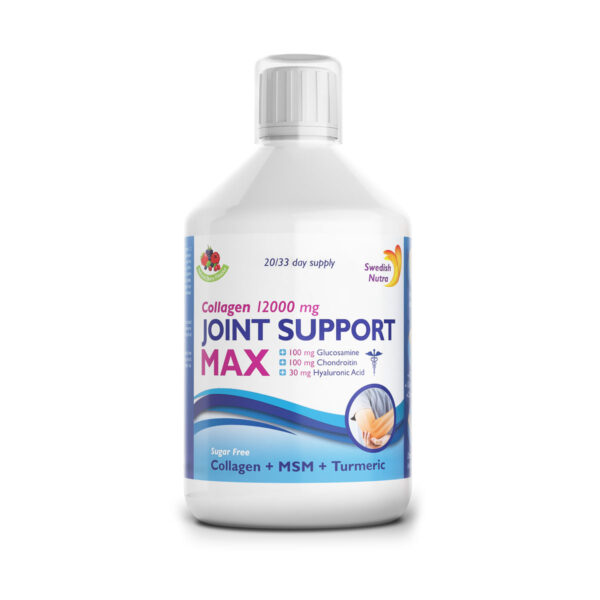
The amazing properties of curcumin – Why is it good for your health?

Turmeric is a spice that has been an essential part of Asian cuisine and Ayurvedic medicine for centuries. Nowadays, scientists and health experts are also increasingly appreciating the extraordinary health benefits of curcumin, the main bioactive component of this plant. It has been found that curcumin can help reduce inflammation, protect the body from oxidative stress and even reduce the risk of cancer.
Let’s take a closer look at why curcumin is so promising and valued, and when we might consider using it.
Anti-inflammatory effect
Curcumin is best known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is the body’s natural defence mechanism against injury and infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to a wide range of health problems such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and even cancer. Curcumin inhibits certain molecules and enzymes involved in inflammatory processes, thereby helping to alleviate the symptoms of inflammatory diseases.
Antioxidant effect
Free radicals are harmful substances that can damage the DNA of cells and cause premature ageing and disease. Curcumin not only neutralises free radicals due to its antioxidant properties, but also increases the activity of the body’s own antioxidant enzymes. This strengthens the body’s defences, helping to prevent the development of chronic diseases.
Liver health
The health of the liver is crucial as it filters toxins from the blood and produces digestive enzymes. Curcumin has been found to have hepatoprotective effects, helping to protect the liver from damage and inflammation. It may be particularly useful for people suffering from fatty liver or other liver diseases.
Cancer prevention and treatment
Cancer research is complex and the anti-cancer properties of curcumin need much more scientific proof. Laboratory studies carried out so far by researchers have shown that curcumin, both in combination with and without anti-cancer drugs, is able to slow the proliferation of cancer cells and promote their destruction. Although these results are still pre-clinical, it opens new possible doors in the fight against cancer.